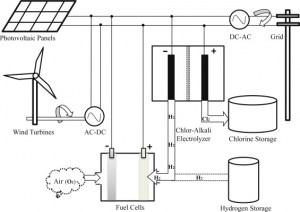
 Alternative energy technologies are receiving significant attention due to diminishing traditional fossil fuel resources and increasing worldwide energy demand. Hybrid renewable energy systems (HRES), which consist of solar, wind and other energy generation and storage units, have proven to be effective in dealing with the intermittent generation and scarce supply of a single renewable resource. Both residential electricity consumption and energy-intensive process industries are studied from the perspective of demand management as well as dispatch optimization.
Alternative energy technologies are receiving significant attention due to diminishing traditional fossil fuel resources and increasing worldwide energy demand. Hybrid renewable energy systems (HRES), which consist of solar, wind and other energy generation and storage units, have proven to be effective in dealing with the intermittent generation and scarce supply of a single renewable resource. Both residential electricity consumption and energy-intensive process industries are studied from the perspective of demand management as well as dispatch optimization.
We collaborate with Professor Nael El-Farra on this project.
Related Publications
- Wang, X., N.H. El-Farra, A. Palazoglu, “Optimal Scheduling of Demand Responsive Industrial Production with Hybrid Renewable Energy Systems,” Renewable Energy, 100, 53-64 (2017).
- Tong, C., A. Palazoglu, N.H. El-Farra, X. Yan, “Energy Demand Management for Process Systems Through Production Scheduling and Control,” AIChE J., 61(11), 3756–3769 (2015).
- Wang, X., N.H. El-Farra, A. Palazoglu, “Proactive Reconfiguration of Heat-Exchanger Super Networks,” Ind. & Eng. Chemistry Research, 54, 9178−9190 (2015).
- Wang, X., A. Palazoglu, N.H. El-Farra, “Operation of Residential Hybrid Renewable Energy Systems: Integrating Forecasting, Optimization and Demand Response,” Applied Energy, 143, 324-335 (2015).
- Wang, X., H. Teichgraber, A. Palazoglu, N.H. El-Farra, “An Economic Receding Horizon Optimization Approach for Energy Management in the Chlor-Alkali Process with Hybrid Renewable Energy Generation,” J. Process Control, 24, 1318-1327 (2014).