We also modelded the fibrous gas diffusion layer as three dimensional impermeable cylindrical fibers randomly distributed for the in-plane directions. Unsteady liquid water behavior is simulated using commercial software FLUENT incorporated with the volume of fluid (VOF) scheme. The results indicate the cross leakage flow occurring in a typical serpentine flow channel could be effective to get rid of the liquid water accumulated in the gas diffusion layer especially under the land area. The characteristics of liquid water discharging from the gas diffusion layer are critical for the water management at the high load operation of the PEM fuel cell. It has been observed that the liquid water is discharged more effectively for the higher hydrophobicity of the fiber surface.
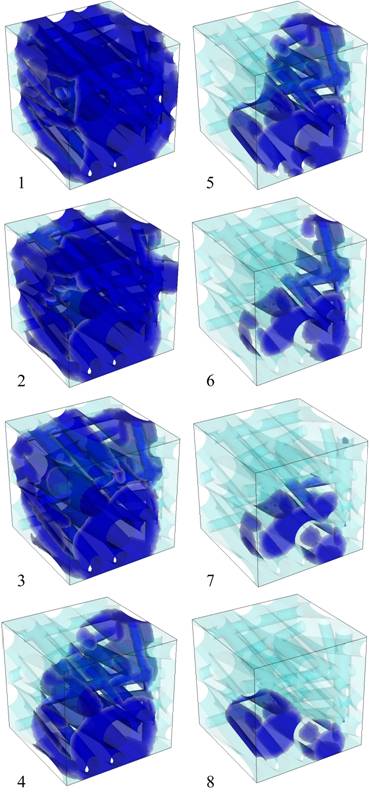
Unsteady liquid water discharging from the gas diffusion layer; the pressure gradient is 6.5 × 105 Pa/m and contact angle is 135 o, time step between each figure is 500 msec.