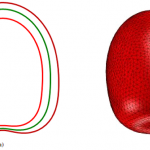
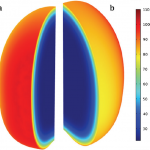
Mathematical modelling is an important tool for designing of food processing systems and optimizing the operational parameters. The modeling results provide important information for the mechanistic understanding of the food processing and for controlling the product quality and. Our research team uses engineering software such as COMSOL Multiphysics and MATLAB to conduction simulation studies. Selected modeling studies include:
- Moisture diffusion within rice kernels during drying
- Three‐dimensional geometric modeling of tomatoes
- Modeling of heat transfer of tomatoes and other fruits during peeling
- Modeling of contact-heating process for cooking a hamburger patty
- Modeling of coupled enzymatic hydrolysis and membrane separation process during the peptides production from protein
- Drying kinetics of grains, nuts, vegetables and fruits
- Thermal inhibition kinetics of enzymes in fruits and vegetables
- Inactivation kinetics of flavus on rough rice
- Determination of effective moisture diffusivity in the walnuts during hot air drying process
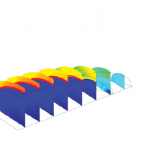
Moisture gradient in the ellipsoid-shaped rough rice grain model after 20 min of heated air drying at 45oC