Additive Manufacturing – Applications and Sustainability

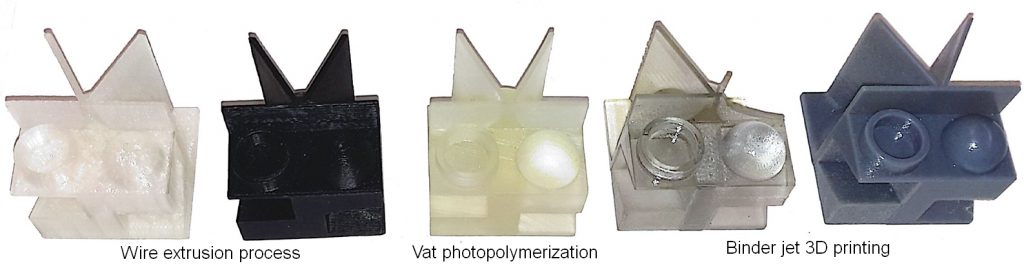
We are investigating surface finishing of additively manufactured implants for veterinary medicine. Abrasive finishing reduces the surface roughness effectively, but studies in the literature are not comprehensively described [Fashanu20]. Grindability of extruded and 3D printed PEEK samples was studied to improve post-processing repeatability and automation [Linke24a]. This is collaborative research with Prof. Denis Marcellin-Little, Surgical & Radiological Sciences, School of Veterinary Medicine, UC Davis.
 Polymer 3D printing can generate physical 3D models of organs to help with training and research studies [Roeth19],[Roeth21]. Its sustainability can be improved by considering printing energy, part dimensions, surface roughness, material recyclability, and waste [Linke23]. This research is performed with Dr. med. Dipl.-Phys. Anjali A. Roeth, ESCAM – European Surgical Center Aachen Maastricht, The Netherlands, University Hospital RWTH Aachen, Germany.
Polymer 3D printing can generate physical 3D models of organs to help with training and research studies [Roeth19],[Roeth21]. Its sustainability can be improved by considering printing energy, part dimensions, surface roughness, material recyclability, and waste [Linke23]. This research is performed with Dr. med. Dipl.-Phys. Anjali A. Roeth, ESCAM – European Surgical Center Aachen Maastricht, The Netherlands, University Hospital RWTH Aachen, Germany.
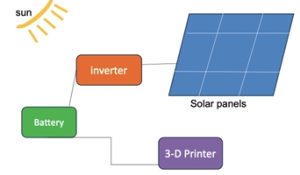 A study with Prof. Erick Ramírez-Cedillo (Tecnológico de Monterrey, Mexico) and Prof. Mohsen Habibi (UC Davis) studies the design of mobile, energy-efficient, and sustainable 3D printing systems that can be used in emergencies and in rural communities to print essential medical and mechanical parts [Linke24b].
A study with Prof. Erick Ramírez-Cedillo (Tecnológico de Monterrey, Mexico) and Prof. Mohsen Habibi (UC Davis) studies the design of mobile, energy-efficient, and sustainable 3D printing systems that can be used in emergencies and in rural communities to print essential medical and mechanical parts [Linke24b].
 Further studies at the Master Lab have looked into environmental impacts and perceived quality of polymer 3D printing [Li17] and energy use during fused deposition modeling [Wang21]. RPTU Kaiserslautern led a Unit Process Life Cycle Inventory on high speed laser directed energy deposition [Ehmsen23].
Further studies at the Master Lab have looked into environmental impacts and perceived quality of polymer 3D printing [Li17] and energy use during fused deposition modeling [Wang21]. RPTU Kaiserslautern led a Unit Process Life Cycle Inventory on high speed laser directed energy deposition [Ehmsen23].
References:
[Ehmsen23] Ehmsen, S., Yi, L., Glatt, M., Linke, B., Aurich, J., Reusable unit process life cycle inventory for manufacturing: high speed laser directed energy deposition. Prod. Eng. Res. Devel. (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11740-023-01197-4
[Fashanu20] Felicia F. Fashanu, Denis J. Marcellin-Little, Barbara S. Linke, Review of Surface Finishing of Additively Manufactured Metal Implants, MSEC2020-8419, Proceedings of the ASME 2020 15th International Manufacturing Science and Engineering Conference, MSEC2020 June 22-26, 2020, Cincinnati, OH, USA
[Li17] Li, Y.; Linke, B.; Voet, H.; Falk, B.; Schmitt, R.; Lam, M.: Cost, sustainability and surface roughness quality – A comprehensive analysis of products made with personal 3D printers, CIRP Journal of Manufacturing Science and Technology, Volume 16, January 2017, Pages 1–11, http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.cirpj.2016.10.001
[Linke23] B Linke, F Fashanu, K Bashayan, RThavi, AA Roeth: Sustainable 3D Printing of Organ Replica for Endoscopy Training and Medical Research, Proc. ASME. MSEC2023, Volume 1: Additive Manufacturing; Advanced Materials Manufacturing; Biomanufacturing; Life Cycle Engineering, V001T04A002, June 12–16, 2023, https://doi.org/10.1115/MSEC2023-101752
[Linke24a] BS Linke, A Georgens, C Romero, TC Garcia and DJ Marcellin-Little, Grindability of extruded and 3D printed PEEK samples, Published Online: September 4, 2024, pp 236-260, https://doi.org/10.1504/IJAT.2024.140961
[Linke24b] B Linke, K Bashayan, E Ramírez-Cedillo, A Armendariz-Rodriguez, M Habibi, A Vargas Martínez, R A Ramirez-Mendoza, Empowering mobile, energy-efficient and sustainable 3d printing systems for emergencies and rural communities, to be published at IMECE 2024
[Roeth19]
[Roeth21] Roeth AA, Garretson I, Beltz M, et al. 3D-Printed Replica and Porcine Explants for Pre-Clinical Optimization of Endoscopic Tumor Treatment by Magnetic Targeting. Cancers (Basel). 2021;13(21):5496. Published 2021 Nov 1. doi:10.3390/cancers13215496
[Wang21] Xiange Wang, Philip Kent Velbis, Barbara Linke, Framework for User-Friendly Modeling of Energy Use in Fused Deposition Modeling, ASME MSEC 2021, MSEC2021-2015
